A. Understanding USB Access Denied Error
What Is USB Access Denied Error?
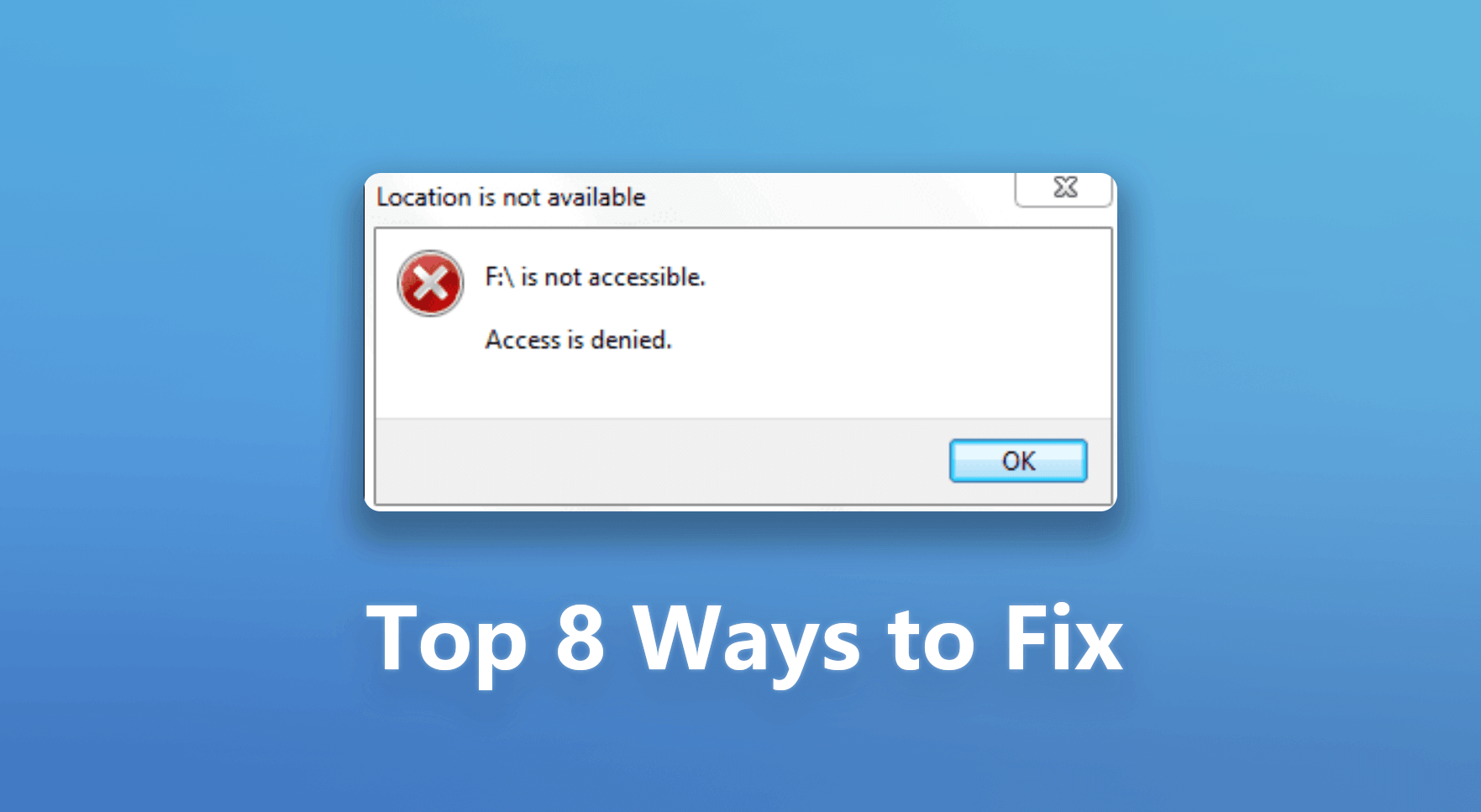
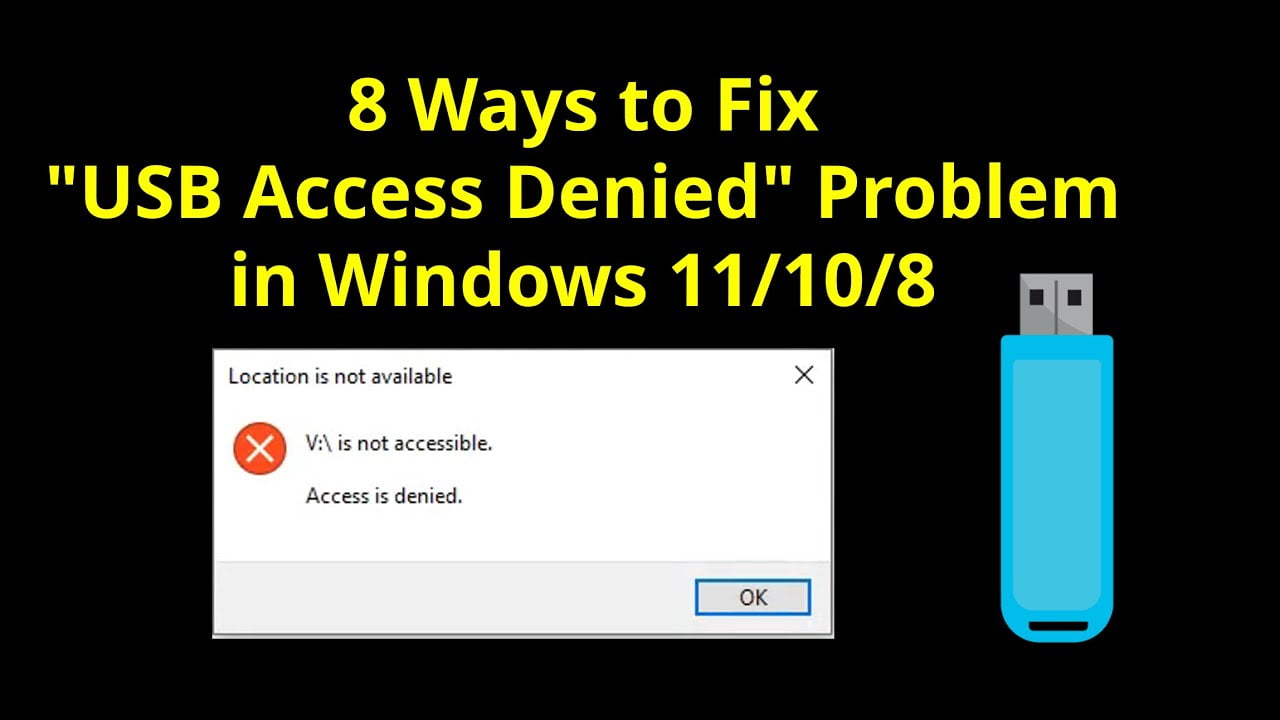
The USB Access Denied error is a common issue encountered by Windows 11 and Windows 10 users when attempting to access a USB drive. It manifests as a restriction preventing users from reading or writing data to the USB device.
A. Reasons Behind “USB Access Denied”
The error may arise due to various reasons, including insufficient user permissions, security settings, or corrupted system files. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for implementing effective solutions.
B. Addressing Access Denied Issues
Methods to Fix USB Drive Access Denied
To resolve the “USB Access Denied” problem, users can employ a variety of methods ranging from adjusting system settings to running advanced diagnostic tools. These solutions aim to provide users with step-by-step guidance in addressing access issues with their USB drives.
This introduction sets the stage for the article by defining the USB Access Denied error, exploring its possible reasons, and hinting at the diverse methods users can employ to fix this issue on Windows 11 and Windows 10 systems.
II. Fixing USB Drive Access Denied in Windows
A. General Troubleshooting Steps
Adjusting Windows Local Group Policy
Modifying the local group policy settings in Windows can be an effective solution to the “USB Access Denied” issue. Users can adjust policies related to removable storage access to grant necessary permissions.
Managing Advanced Security Settings for USB
Delving into advanced security settings allows users to customize permissions for the USB drive. Adjusting these settings can help resolve access-denied problems by granting the necessary rights to the user.
Changing Drive Letter for USB Access
Sometimes, changing the drive letter assigned to the USB device can circumvent access issues. This simple adjustment can be performed through the Disk Management utility in Windows.
Running Disk Checking to Fix USB Drive
Running a disk check on the USB drive helps identify and repair potential file system errors. This method ensures the drive is in a healthy state and can be accessed without encountering an access denied error.
B. Advanced Solutions
Editing Local Group Policy
Further customization of local group policy settings may be required in certain cases. Users can navigate through the group policy editor to make specific adjustments that resolve the “USB Access Denied” problem.
Utilizing Error Checking Tool
Windows provides an error-checking tool that can scan and fix errors on the USB drive. This method helps in identifying and repairing issues that may be contributing to the access denied problem.
Running Chkdsk for USB Drive
Chkdsk (Check Disk) is a command-line utility that can be used to check for and fix errors on the USB drive. Running this tool ensures the integrity of the drive’s file system, addressing potential access issues.
C. Reinstallation and Reset
Reinstalling USB Drivers
A corrupted or outdated USB driver can lead to access-denied problems. Reinstalling the USB drivers can resolve this issue by ensuring the correct and updated drivers are in place.
Resetting USB to Factory Settings
For persistent issues, resetting the USB settings to factory defaults may be necessary. This step can be performed through device settings or utilities provided by the USB manufacturer.
This section outlines a variety of methods, both basic and advanced, that users can employ to fix the “USB Access Denied” problem in Windows 11 and Windows 10. Each method is succinctly explained, providing users with practical steps to troubleshoot and resolve access issues with their USB drives.
III. Data Recovery for Inaccessible USB Drive

How to Recover Data from an Inaccessible USB Drive
Recovering data from an inaccessible USB drive is a critical aspect, especially when troubleshooting the “USB Access Denied” problem. Users may encounter situations where fixing the access issues results in potential data loss. In such cases, it’s essential to follow proper data recovery steps to retrieve important files.
Users can utilize specialized data recovery software to scan the inaccessible USB drive for lost or deleted files. These tools are designed to recover data from various storage devices, including USB drives, even when access is denied.
The steps generally involve:
- Installing a reputable data recovery tool on the computer.
- Connecting the inaccessible USB drive to the computer.
- Launching the data recovery software and selecting the USB drive.
- Initiating a scan to identify recoverable files on the drive.
- Previewing and selecting the desired files for recovery.
- Choosing a safe location to save the recovered files.
It’s crucial to avoid writing new data to the USB drive during the recovery process to prevent overwriting existing data.
By following these straightforward steps, users can successfully recover their valuable data from an inaccessible USB drive, ensuring that important files are not permanently lost during the troubleshooting process.
I. USB Access Denied Issues on Windows
A. Overview of USB Access Denied Errors
USB access denied errors on Windows can disrupt the smooth functioning of external devices, creating obstacles in file transfer and device recognition. Understanding the root causes and specific errors is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
B. Common Reasons for USB Access Denied
Driver Issues:
Outdated or corrupted USB drivers can lead to access-denied problems. Ensuring drivers are up-to-date is a fundamental step in addressing this issue.
Permissions Restrictions:
User account permissions may restrict access to USB devices. Adjusting user permissions is essential for overcoming access-denied errors.
Security Software Interference:
Overzealous antivirus or security software may wrongly identify USB devices as threats, resulting in access denial. Configuring security software settings is necessary for smooth USB functionality.
Device Compatibility:
Incompatible or faulty USB devices can trigger access denied errors. Verifying device compatibility and integrity is vital for resolving this issue.
Administrator Restrictions:
Certain USB access denied errors stem from administrator-imposed restrictions. Understanding and modifying these restrictions is key to resolving such errors.
Group Policy and Registry Settings:
Group policy and registry configurations may impose restrictions on USB access. Adjusting these settings is a nuanced but effective approach to tackling access-denied issues.
II. Troubleshooting USB Access Denied in Windows 10
A. Adjusting Group Policy
Accessing Group Policy Editor:
Navigate to the Group Policy Editor in Windows 10 by typing “gpedit.msc” in the Run dialog. This tool allows users to configure system settings, including those related to USB access.
Configuring Removable Storage Access:
Within the Group Policy Editor, locate and modify the policies related to removable storage. Specifically, check policies such as “All Removable Storage classes: Deny all access” and adjust them to allow access.
B. Managing Security Settings
User Account Control (UAC) Settings:
Adjusting UAC settings can mitigate USB access denied errors. Go to Control Panel > Security and Maintenance > Change User Account Control settings, and lower the slider to a more permissive level.
Permission Adjustments:
Navigate to the properties of the USB drive or device in File Explorer. Under the Security tab, ensure that the current user or relevant user groups have the necessary permissions. Adjust as needed.
C. Running Error-Checking Tools
Using CHKDSK Command:
Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the CHKDSK command with the parameter specifying the target USB drive (e.g., “chkdsk E: /f”). This command checks and repairs file system errors on the USB drive.
Windows Error Checking Tool:
Alternatively, use the built-in Windows Error Checking tool. Right-click on the USB drive in File Explorer, go to Properties > Tools and click on “Check” under Error checking.
This section provides concise steps for troubleshooting USB access denied issues on Windows 10, including adjusting group policy settings, managing security configurations, and running error-checking tools to ensure a streamlined resolution process.
III. Solutions for USB Access Denied in Windows 7
A. Addressing Administrator Restrictions
Run as Administrator:
When encountering USB access denied issues in Windows 7, try running applications or accessing USB devices with administrative privileges. Right-click on the application or device and select “Run as Administrator.”
Administrator Account Settings:
Check the user account type; ensure it has administrator privileges. If necessary, switch to an administrator account to troubleshoot and resolve access issues.
B. Group Policy Adjustments
Accessing Local Group Policy Editor:
Open the Local Group Policy Editor by typing “gpedit.msc” in the Run dialog. Navigate through User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access.
Modify Group Policy Settings:
Within Removable Storage Access, adjust policies such as “All Removable Storage classes: Deny all access.” Modify these settings to grant access or configure policies based on specific user needs.
C. Modifying Registry Settings
Opening Registry Editor:
Access the Registry Editor by typing “regedit” in the Run dialog. Be cautious when editing the registry, as it directly impacts system settings.
Navigate to USB Key:
In the Registry Editor, navigate to “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\USBSTOR.” Check for any restrictive values in the right pane and modify them accordingly.
This section offers practical steps for resolving USB access denied issues on Windows 7. Users can address administrator restrictions by running applications with elevated privileges, adjusting user account settings, and exploring group policy adjustments and registry modifications to grant the necessary USB access.
IV. Resolving USB Access Denied on Windows 11
A. Compatibility and Permissions
Checking USB Device Compatibility:
Ensure the USB device is compatible with Windows 11. Some older devices may not be fully supported, leading to access denied issues. Consider updating drivers or using a compatible device.
Verifying User Permissions:
Check user permissions for accessing USB devices. Navigate to the Security tab in the properties of the USB device, and ensure that the current user or user groups have the required permissions.
B. Advanced Troubleshooting Methods
Using Device Manager:
Open Device Manager and locate the USB device that is experiencing access denied issues. Right-click on the device, select “Uninstall device,” and then reconnect the USB device to allow Windows to reinstall the drivers.
Updating Firmware:
For certain USB devices, updating the firmware may resolve compatibility issues. Check the manufacturer’s website for firmware updates and follow their instructions for installation.
C. Utilizing Windows 11 Group Policy
Accessing Group Policy Settings:
Open the Local Group Policy Editor by typing “gpedit.msc” in the Run dialog. Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access.
Adjusting Group Policy:
Within Removable Storage Access, modify policies such as “All Removable Storage classes: Deny all access” based on the user’s requirements. Ensure that policies are configured to permit USB access as needed.
This section offers concise guidance for users encountering USB access denied issues on Windows 11. It covers checking compatibility and permissions, advanced troubleshooting using Device Manager and firmware updates, and adjusting group policy settings to ensure a seamless USB experience.
V. USB Access Denied by Administrator
Administrator Account Control (UAC):
In scenarios where USB access is denied by the administrator, review the User Account Control (UAC) settings. Lowering the UAC level in Control Panel > Security and Maintenance may alleviate access restrictions.
Account Types and Permissions:
Ensure the user account has administrator privileges. If necessary, switch to an administrator account to troubleshoot and resolve access denied issues.
B. Overcoming Access Barriers
Run Applications as Administrator:
Right-click on applications or USB devices and select “Run as Administrator” to execute them with elevated privileges. This may bypass access barriers imposed by administrator restrictions.
Administrator Password Confirmation:
Some actions may prompt for administrator password confirmation. Ensure that the correct password is entered to authorize USB access.
VI. Group Policy and USB Access Denied in Windows 10
A. Navigating Group Policy Settings
Accessing Local Group Policy Editor:
Open the Local Group Policy Editor by typing “gpedit.msc” in the Run dialog. Navigate through User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access.
Examining Group Policy Entries:
Within Removable Storage Access, evaluate entries such as “All Removable Storage classes: Deny all access.” Adjust these policies based on user requirements to permit USB access.
B. Customizing USB Permissions
Security Settings for USB Devices:
In File Explorer, navigate to the properties of the USB device. Under the Security tab, ensure that the current user or relevant user groups have the necessary permissions. Adjust as needed for seamless USB access.
Group Policy Adjustments:
Leverage the Group Policy Editor to modify settings related to USB access. Tailor these policies to align with user preferences while ensuring security considerations are met.
VII. Registry Settings for USB Access Denied
A. Modifying Registry Entries
Opening Registry Editor:
Access the Registry Editor by typing “regedit” in the Run dialog. Caution is advised when editing the registry, as it directly impacts system settings.
Navigating to USB Registry Key:
In the Registry Editor, navigate to “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\USBSTOR.” Check for any restrictive values in the right pane and adjust them accordingly.
The Registry settings provide a granular approach to resolving USB access-denied issues, allowing users to modify specific entries to ensure seamless connectivity and data transfer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing the “USB Access Denied” problem in Windows 11/10 involves a systematic approach, from understanding the error and its causes to implementing practical solutions. By adjusting local group policies, managing security settings, and utilizing advanced tools like chkdsk, users can overcome access issues and regain control over their USB drives.
Additionally, the importance of data recovery cannot be overstated, as resolving access problems may carry the risk of potential data loss. By following the outlined steps for data recovery from an inaccessible USB drive, users can ensure that their valuable files remain intact throughout the troubleshooting process.
This comprehensive guide empowers users to navigate and resolve the complexities of the “USB Access Denied” issue, ultimately enhancing the functionality and reliability of USB drives on Windows systems.





4 thoughts on “Top 9 Ways to Fix “USB Access Denied” Problem in Windows 11/10”