When switching from a Windows PC to a Mac, one of the most common questions is, “How do I Open Task Manager on Mac?” The Task Manager on Windows is a crucial tool for monitoring system performance, managing running applications, and troubleshooting issues. The equivalent functionality exists on a Mac, but it’s accessed differently. This guide provides detailed instructions on accessing and using Task Manager-like features on a Mac.
Understanding the Equivalent of Task Manager on Mac
The Mac operating system (macOS) doesn’t have a direct counterpart to the Windows Open Task Manager on Mac. However, macOS offers tools that provide similar functionality, including the Activity Monitor, Force Quit Applications, and Terminal Commands. These tools allow users to monitor system resources, manage running applications, and troubleshoot issues effectively.
1. Using Activity Monitor: The Mac Task Manager
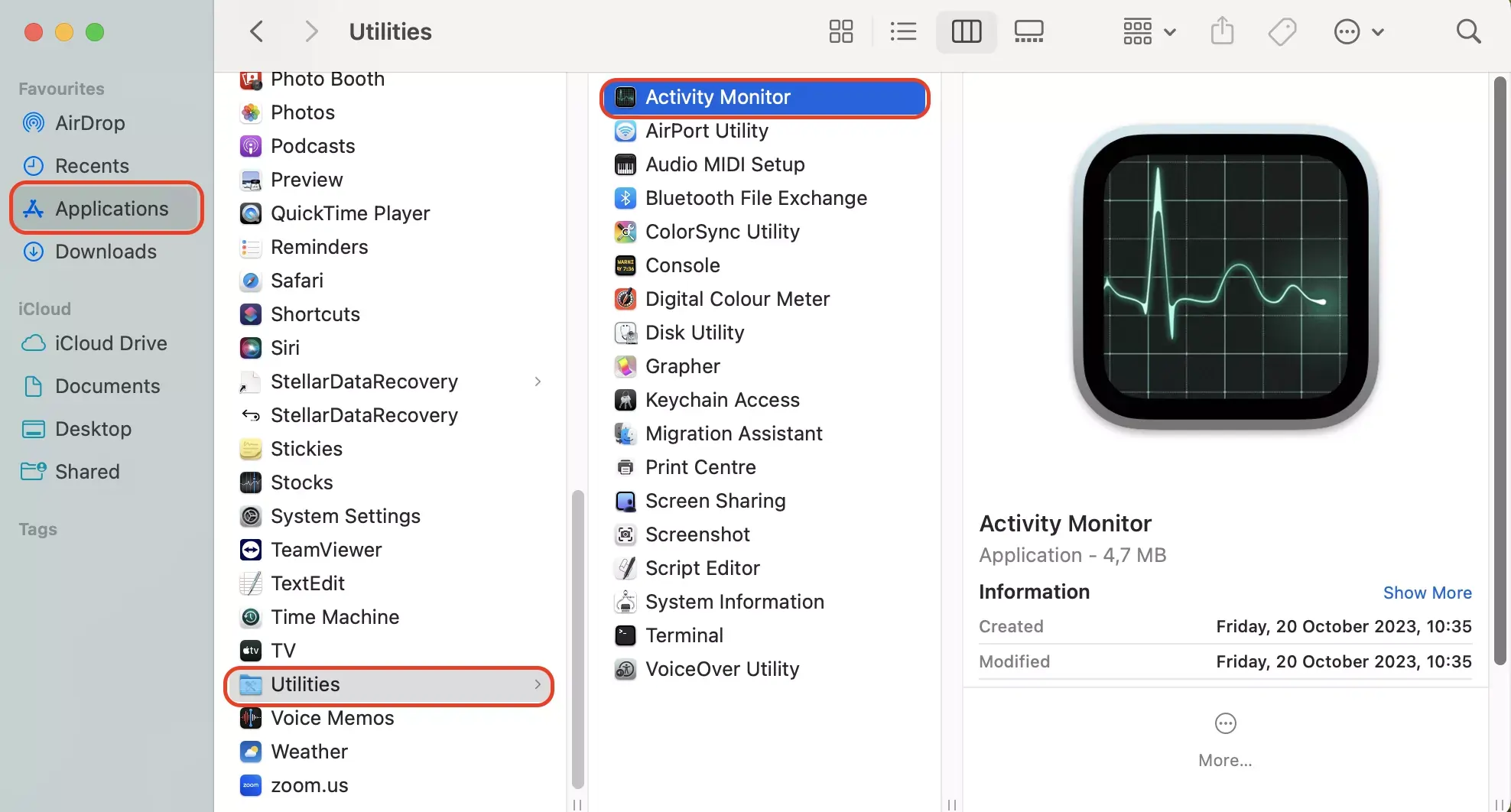
What Is Activity Monitor?
Activity Monitor is the closest equivalent to the Open Task Manager on Mac. It provides detailed insights into your Mac’s performance, including CPU, memory, energy, disk, and network usage.
How to Open Activity Monitor
- Method 1: Via Spotlight Search
- Press
Command + Spaceto open Spotlight Search. - Type “Activity Monitor” and press Enter.
- Press
- Method 2: Through the Applications Folder
- Open
Finderand navigate toApplications. - Go to the
Utilitiesfolder. - Double-click on
Activity Monitor.
- Open
Features of Activity Monitor
- CPU Tab: This tab displays the processes using the most CPU resources. It helps you identify which applications are slowing down your Mac.
- Memory Tab: This tab shows the amount of RAM being used by each application. It helps manage memory-intensive applications.
- Energy Tab: Monitors energy consumption, which is especially useful for MacBook users to extend battery life.
- Disk Tab: Lists the data read and written by different processes.
- Network Tab: Tracks data sent and received by each application over the network.
Graph TD;
- A[Open Activity Monitor] –> B[Spotlight Search]
A --> C[Applications Folder]
B --> D[Command + Space]
C --> E[Finder > Applications > Utilities]
D --> F[Type and Open Activity Monitor]
E --> G[Double-click Activity Monitor]
2. Force Quit Applications: A Quick Fix for Unresponsive Apps
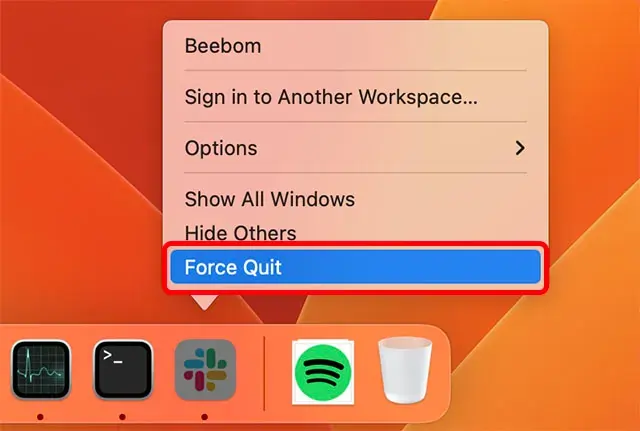
What Is Force Quit Applications?
When an application becomes unresponsive, the quickest solution is to use the Force Quit feature, which is similar to the “End Task” option in Windows Open Task Manager on Mac.
How to Use Force Quit Applications
- Method 1: Using the Apple Menu
- Click on the
Applelogo in the top-left corner of the screen. - Select
Force Quitfrom the dropdown menu. - Choose the unresponsive application and click.
Force Quit.
- Click on the
- Method 2: Keyboard Shortcut
- Press
Command + Option + Escapesimultaneously. - Select the unresponsive app and click.
Force Quit.
- Press
When to Use Force Quit
Force Quit should be used when an application is completely unresponsive and cannot be closed normally. However, be aware that unsaved data may be lost.
3. Using Terminal Commands for Advanced Task Management
Introduction to Terminal
Terminal is a powerful tool on macOS that allows you to execute commands to manage your system. It’s more advanced than Activity Monitor and Force Quit and is suitable for users comfortable with command-line interfaces.
Common Terminal Commands for Task Management
top: Provides a real-time view of system processes, similar to the Activity Monitor’s CPU tab.ps -ax: Lists all running processes. You can find the Process ID (PID) of an application here.kill [PID]: Terminates a specific process by its PID. For example,kill 1234it would terminate the process with PID 1234.
How to Open Terminal
- Method 1: Via Spotlight Search
- Press
Command + Spaceto open Spotlight Search. - Type “Terminal” and press Enter.
- Press
- Method 2: Through the Applications Folder
- Open
Finderand navigate toApplications. - Go to the
Utilitiesfolder. - Double-click on
Terminal.
- Open
4. Monitoring System Performance: CPU, Memory, and More
Why Monitor System Performance?
Monitoring system performance is essential for maintaining your Mac’s health. It helps you identify resource-hogging applications and potential issues before they cause serious problems.
Tools for Monitoring Performance
- Activity Monitor: As discussed, it provides a comprehensive system performance overview.
- iStat Menus: A third-party application that offers more detailed and customizable monitoring options, including real-time graphs in your menu bar.
Understanding CPU Usage
High CPU usage can slow down your Mac. In Activity Monitor, the CPU tab shows which processes consume the most CPU resources. If an application consistently tops the list, it may need to be optimized or closed.
Managing Memory Usage
The Memory tab of Activity Monitor shows how your RAM is being used. If your Mac runs slowly, it might be due to excessive memory usage by specific applications. You can close or manage these applications to free up memory.
5. Energy Consumption: Managing Battery Life
Why Monitor Energy Consumption?
Battery life is crucial for MacBook users. Monitoring energy consumption can help you identify apps that drain your battery quickly.
Energy Tab in Activity Monitor
The Energy tab in Activity Monitor lists all running processes and their impact on your Mac’s battery. Apps with high energy impact should be used sparingly when running on battery power.
Tips to Extend Battery Life
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Apps running in the background can drain your battery.
- Adjust Display Brightness: Lowering your screen brightness can significantly extend battery life.
- Use Energy Saver Mode: Enable this mode
System Preferencesto optimize battery usage.
6. Managing Network Usage on Mac
Importance of Network Monitoring
Monitoring network usage helps you understand which applications are using your internet bandwidth. This is especially important if you are on a limited data plan or experiencing slow internet speeds.
Network Tab in Activity Monitor
The Network tab shows the data sent and received by each process. If you notice an application consuming excessive bandwidth, you can close it to improve your network performance.
Using Terminal for Network Monitoring
nettop: A command that provides a real-time overview of network connections and data usage.iftop: A third-party command-line tool that shows bandwidth usage on your network interfaces.
Conclusion
Navigating task management on a Mac may seem different from what you’re used to on a Windows PC. However, with tools like Activity Monitor, Force Quit, and Terminal, you have everything you need to manage your system effectively. Whether you’re monitoring CPU usage, working memory, or controlling network activity, these tools ensure your Mac runs smoothly.
FAQs
1. Can I use Task Manager on a Mac?
MacOS does not have a direct Task Manager equivalent, but you can use Activity Monitor, Force Quit, and Terminal for similar functionality.
2. How do I force quit an application on a Mac?
You can force quit an app using the Command + Option + Escape shortcut or through the Apple menu by selecting Force Quit.
3. What is Activity Monitor used for?
Activity: Monitor your Mac’s CPU, memory, energy, disk, and network usage, helping you manage system resources effectively.
4. How do I open Terminal on a Mac?
You can open Terminal by using Spotlight Search (Command + Space and typing “Terminal”) or by navigating through the Applications > Utilities folder.
5. How do I check my Mac’s battery usage?
Battery usage is shown in the Energy tab of Activity Monitor, which shows the energy impact of running applications.




