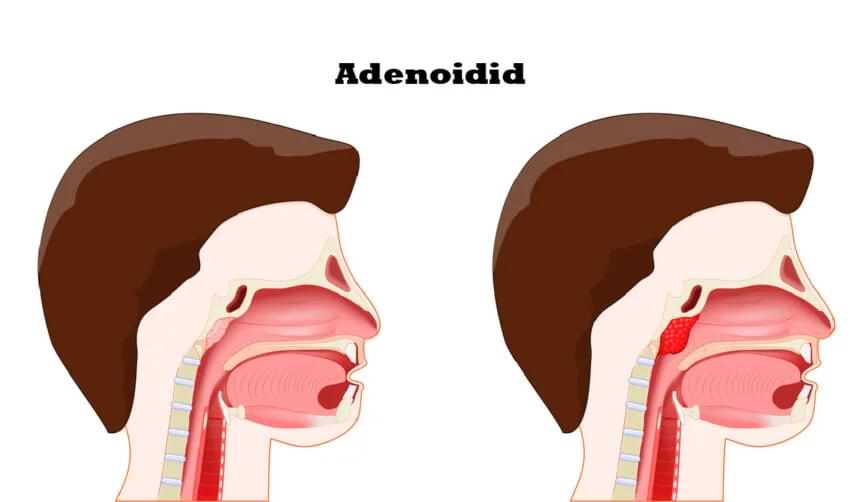
Introduction
Adenoiditis means the swelling or infection of the adenoids, small glands at the back of the nose. These glands are essential for fighting germs during early childhood, but they can sometimes cause health issues when they get bigger or infected. This is something parents should know about, as it can cause breathing problems, repeated infections, and other issues in kids. Adults can also have similar problems, but it’s less common.
In this easy-to-follow guide, we’ll explain what adenoidid is, its role in the body, what causes it, signs to look for, how doctors diagnose it, treatment options, and how to prevent it so that you can make wise health choices for yourself or your child.
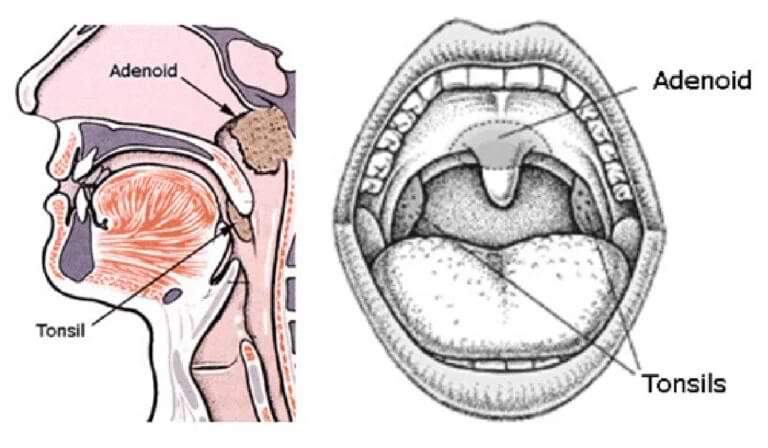
What Are Adenoids?
Adenoids are small lumps of tissue located high in the throat, behind the nose, and cannot be seen directly through the mouth. They are part of the immune system and help protect the body from germs. Adenoids are like tonsils but are located behind the nasal passages, while tonsils are at the back of the throat. Adenoids help clean the air we breathe and stop infections before they reach the lungs.
What Is Adenoidid?
Adenoiditis is when the adenoids become swollen, often because of an infection, allergy, or irritation. This swelling can block air from passing through the nose, causing a stuffy nose, snoring, or trouble sleeping. It’s more common in kids aged 3 to 7 because their adenoids are bigger and more active. As kids grow, adenoids shrink, so adults usually don’t have serious problems unless they have allergies or sinus issues.
What Do Adenoids Do?
Adenoids help young children fight infections by trapping germs that enter through the nose. They also help the body make antibodies, which are proteins that fight sickness. Healthy adenoids support good breathing, especially while sleeping. By stopping many infections early, adenoids play a crucial role in protecting a child’s overall health.
Causes of Adenoiditis
1. Viral Infections
Viruses like the flu, cold viruses, or adenovirus can cause the adenoids to swell. The swelling is the body’s way of fighting off the infection, but it can cause breathing or ear issues.
2. Bacterial Infections
Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae can also infect the adenoids. These infections can be more severe and often require antibiotics. If left untreated, they can recur.
3. Allergies
Allergies to dust, pollen, or pet hair can make adenoids swell, even if there is no infection. This can happen in kids with frequent allergies.
4. Environment
Breathing in polluted air or secondhand smoke can also cause adenoids to swell. Smoke from cigarettes is a major cause of ear, nose, and throat problems in kids.
5. Family and Health History
If others in the family have similar problems, children may be more likely to experience them as well. A weak immune system can also make infections more common.
Symptoms ofAdenoiditisd
In Children
Kids may have:
-
Stuffy or blocked nose
-
Breathing through the mouth
-
Snoring or restless sleep
-
Frequent ear infections
Swollen adenoids can block the tubes that connect the ears, causing fluid buildup and hearing problems.
In Adults
Though rare, adults can have:
-
Constant stuffy nose
-
Sinus pressure
-
Repeated sinus infections
-
Hearing trouble
What Happens If It’s Not Treated?
If not treated, adenoids can cause:
-
Facial changes (long face, open-mouth habit)
-
Crooked teeth or jaw problems
-
Speech delays
-
Sleep apnea (breathing stops during sleep)
-
Slower growth and brain development in children
How Do Doctors Diagnose Adenoiditis
Doctors will ask about symptoms, breathing issues, and the frequency of infections.
2. Exam Tools
Doctors might use:
-
A small camera (nasal endoscope) to look inside the nose
-
X-rays or CT scans to see how big the adenoids are
-
Hearing tests to determine if ear infections are common
-
Swab test if they suspect bacteria
Treatment Options
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
Mild cases can be treated with:
-
Saline (saltwater) sprays to clear the nose
-
Allergy medicines (antihistamines)
-
Decongestants
-
Antibiotics (for bacterial infections)
-
Nasal sprays with steroids to reduce swelling
2. Home Remedies
Some helpful home care includes:
-
Steam inhalation for a stuffy nose
-
Saltwater gargles for throat relief
-
Herbal teas like chamomile or peppermint
-
Eating probiotics like yogurt to boost immunity
3. Surgery (Adenoidectomy)
When Is It Needed?
Surgery is recommended if:
-
Breathing is tough
-
Infections keep coming back
-
The child has sleep apnea
The Surgery
The doctor removes the adenoids through the mouth under general anesthesia. The surgery takes about 20–30 minutes and leaves no external cuts.
Recovery
-
Most kids feel better in a few days
-
Eat soft food and drink lots of water
-
Mild pain is normal
-
Follow the doctor’s advice and attend follow-ups
Long-Term Outlook
With the proper care, the outlook is excellent. Most children stop having symptoms as the adenoids shrink with age. After surgery, breathing improves, sleep gets better, and infections reduce. Sometimes, adenoids can grow back, but that’s rare.
How to Keep Adenoids Healthy
-
Eat healthy foods rich in vitamins
-
Drink lots of water
-
Wash your hands often to stop germs
-
Stay away from smoke and allergens
-
Visit the doctor regularly for checkups
Read Also: A Book On Consignment Inventory System For Hospitals: A Complete Guide
Conclusion
Adenoiditis may not be widely known, but it can cause significant problems, especially in children. Recognizing signs early and getting the proper treatment can prevent serious health issues. Whether using medicines, home care, or surgery, adenoiditis is manageable, and the long-term results are usually excellent. Parents should constantly monitor their child’s breathing and seek medical attention when necessary.
FAQs About Adenoidid
What is adenoidid?
It’s the swelling or infection of adenoids, which are small glands behind the nose. It can cause breathing and ear problems, especially in kids.
What causes it in children?
Common causes include viruses, bacteria, allergies, smoke, or family history.
What symptoms should I watch for?
Blocked nose, mouth breathing, snoring, poor sleep, ear infections, and sometimes speech or dental issues.
How is it treated?
Mild cases: sprays, allergy meds, or antibiotics. Severe cases: surgery (adenoidectomy).
Can adults get adenoids?
Yes, but it’s rare. Adults may develop it due to sinus or allergy issues. Treatment is similar to that of children.