Section 5: The Command Prompt: What It Is and How to Use It on a Dell System
-
Introduction to Command Prompt on Dell Systems:
- Understand how to Command. Prompt functions within the Dell ecosystem.
- Learn about Dell-specific commands and features.
-
Optimizing Dell System Performance:
- Utilize Command. Prompt for system maintenance and performance enhancement on Dell devices.
- Explore commands tailored for Dell hardware diagnostics.
-
Dell-Specific Commands:
- Identify commands that are unique to Dell systems.
- Learn how these commands can be used for troubleshooting and customization.
-
Accessing Command Prompt on Dell Systems:
- Understand the various methods to open Command. Prompt on Dell computers.
- Explore shortcuts and quick access options.
-
Common Commands for Dell Users:
- Discover a set of commonly used commands beneficial for Dell system users.
- Explore commands related to hardware information and diagnostics.
-
Integration with Dell Support:
- Learn how Command Text can be used in conjunction with Dell support services.
- Explore commands that facilitate communication with Dell technical support.
-
Backup and Recovery with Command Prompt:
- Use Command Text for Dell-specific backup and recovery operations.
- Understand commands related to data protection and system restoration.
-
Advanced Troubleshooting on Dell Systems:
- Explore advanced Command Text usage for in-depth troubleshooting on Dell devices.
- Learn commands that address specific Dell system issues.
Understanding how to leverage the Command Text on Dell systems provides users with tailored tools for optimal performance, efficient troubleshooting, and seamless integration with Dell-specific features. This section is a guide for Dell users to maximize the benefits of the Command Text in their computing environment.
[Windows 11/10] How to Check the Wi-Fi Password on Your Computer
If you find yourself needing to reconnect a device or share your Wi-Fi credentials, knowing how to retrieve the Wi-Fi password on your Windows 11 or 10 computer is essential. Here’s a straightforward guide to help you access this information:
-
Using Command Prompt:
- Open Command Text with administrative privileges by right-clicking on the Start button and selecting “Command Text (Admin)” or “Windows PowerShell (Admin).”
- Type the following command:
netsh wlan show profiles.
- Identify your Wi-Fi network name (SSID) and run the command:
netsh wlan show profile name="YourNetworkName" key=clear.
- Under “Key Content,” you’ll find the Wi-Fi password.
|
-
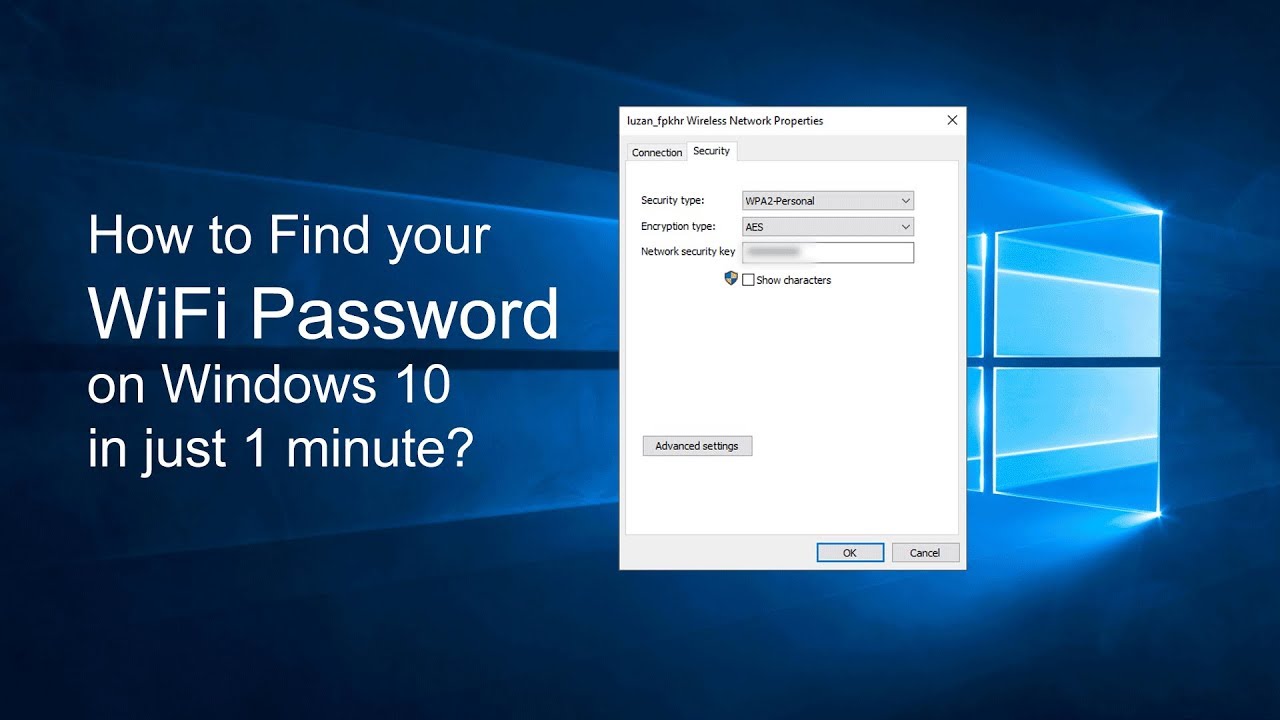
Viewing Network Properties:
- Right-click on the network icon in the system tray and select “Open Network & Internet settings.”
- Go to “Wi-Fi” and click on “Manage known networks.”
- Select your Wi-Fi network, click “Properties,” and under the “Security” tab, check the box that says “Show characters.” The Wi-Fi password will now be visible.
|
-
Using PowerShell:
- Open PowerShell as an administrator.
- Run the command:
netsh wlan show profiles | Select-String "SSID_NAME".
- Replace “SSID_NAME” with your actual network name.
- Run the command:
netsh wlan show profile name="YourNetworkName" keyMaterial=clear.
- Look for the “Key Content” field to find your Wi-Fi password.
|
-
Accessing Router Settings:
- If you have access to your router’s web interface, log in using a web browser.
- Navigate to the wireless settings or security section to find the Wi-Fi password.
|
-
Using Third-Party Software:
- Several third-party tools provide a user-friendly interface to view saved Wi-Fi passwords.
- Be cautious and ensure the software is reputable before downloading and using it.
|
Remember to handle Wi-Fi passwords with care and only share them with trusted individuals. These methods offer different approaches to retrieving your Wi-Fi password, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your preferences and technical comfort level.
Command Prompt Download
The Command Text, a powerful tool for executing commands on Windows operating systems, comes pre-installed with every Windows version. No separate download is required. To access it, simply press, type “cmd,” and press Enter. However, if you are looking for an alternative or enhanced command-line experience, third-party terminal emulators like ConEmu or Cmder are available for download. These tools provide additional features, customization options, and a more user-friendly interface while retaining the core functionality of the native Command Text.
Command Prompt Online
The Command Text itself is a local tool, and there is no direct online version. However, various online resources and forums offer extensive command references, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides for users seeking assistance with Command Text-related queries. Online platforms like Stack Overflow, Microsoft’s official documentation, and tech forums provide valuable insights and solutions shared by the community.
Command Prompt Windows 7
In Windows 7, the Command Text functions similarly to later versions. To access it, click the Start button, type “cmd” in the search bar, and press Enter. Windows 7 includes many of the commands found in later versions, making it a reliable tool for basic to advanced system tasks. However, users are encouraged to consider upgrading to a more recent Windows version for access to the latest features, security updates, and improved performance.
Command Prompt Android
While Android operating systems primarily use graphical interfaces, users can access a command-line interface through the Android Debug Bridge (ADB). ADB is a versatile command-line tool that allows communication between a computer and an Android device. To use Command Text-like functionalities on Android, users can install terminal emulator apps from the Google Play Store, such as Termux, which provides a Linux-like environment with a command-line interface for executing various commands and scripting.
Understanding the nuances of Command Text across different platforms empowers users to leverage its capabilities efficiently, from basic file operations to advanced system configurations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, retrieving your Wi-Fi password on a Windows 11 or 10 computer is a straightforward process with various methods to suit different preferences. Whether you opt for the Command Text command-line efficiency, navigate through the system settings, utilize PowerShell for advanced users, access your router’s web interface, or choose a user-friendly third-party tool, the key lies in selecting the method that aligns with your comfort level and specific requirements.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effortlessly access and share your Wi-Fi credentials when needed, ensuring a seamless and convenient connectivity experience on your Windows device.






2 thoughts on “How to Use Best Command Prompt in Windows 10/11”